
Positive expression of both prostate‐specific antigen and prostate‐specific acid phosphate were found in the inner cells of both male cases. In Case 2, androgen receptor showed intermediate positivity in the inner cells estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor were positive in the outer cells.

In Case 1, androgen receptor and estrogen receptor were negative progesterone receptor was focally positive in both the inner and outer cells. Immunohistochemically, the inner cells of the tumor glands were positive for cytokeratin CAM5.2, CEA, EMA, olfactomedin‐4 and alpha‐methylacyl‐coenzyme A racemase the outer cells were positive for p63 and cytokeratin high molecular weight. Microscopically, all three cases showed the bilayered structure of tumor glands and corpora amylacea in the glandular lumens. Case 3 was a 45‐year‐old man with a history of first‐degree AV block and sinus bradycardia. Case 2 was a 76‐year‐old man with an implanted pacemaker for complete atrioventricular block. Case 1 was a 36‐year‐old woman without any clinical history. We pathologically investigated three autopsy cases of cystic tumor of the atrioventricular node (CTAVN) with sudden death. The obvious key question is how this arrangement is being achieved.Įarly cardiac development starts with the formation of a primary heart tube from the cardiogenic mesoderm (Fig 1⇓) this topic has been reviewed recently.4 The primary heart … Departures from these tenets have led to a confusing and fruitless search for so-called “cardiac specialized tissues” during development. Rather, it is of paramount importance to appreciate that the arrangement of myocyte populations, with distinct contractile, conductive, and pacemaking properties, establishes the coordinated activation of the heart. In the early embryonic heart tube, an ECG, similar to an adult ECG, can be recorded, indicating the presence of sequentially activated chambers.3 Given this observation, it is as confusing to accept the presence of a conduction system because it is functionally present as it is to deny its existence because it is not morphologically recognizable. The myocytes of the conduction system share with those of the ordinary working myocardium four basic elements: (1) contraction, (2) autorhythmicity, (3) intercellular conduction, and (4) electromechanical coupling. Classic reports cover the anatomy,1 pathology,1 and histology2 of the adult and developing conduction system. With a delay, the impulse is then rapidly transmitted from the AVN via the bundle branches and PPN to ensure a coordinated activation of the ventricular myocardium from apex to base.
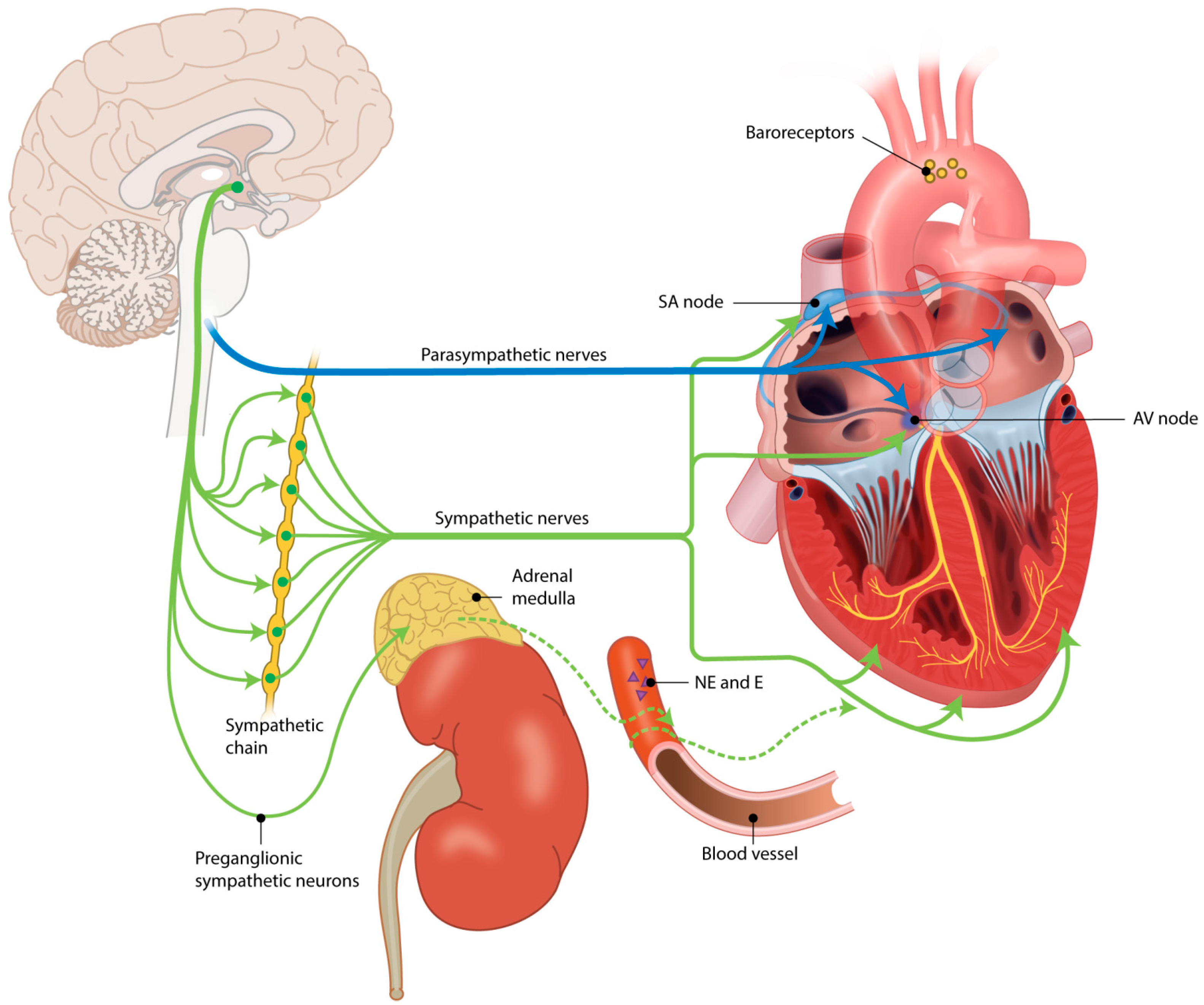
The impulse is subsequently conducted, via the atrial myocardium, which in this sense is part of the conduction pathway as well, toward the AVN. The SAN, which contains the leading pacemaker, generates the impulse. The conduction system comprises separate components with distinct functions. In the formed heart, it is convention to distinguish working myocardium (the primary function of which is contraction) from the conduction system (the primary function of which is the generation and conduction of the electrical impulse).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
